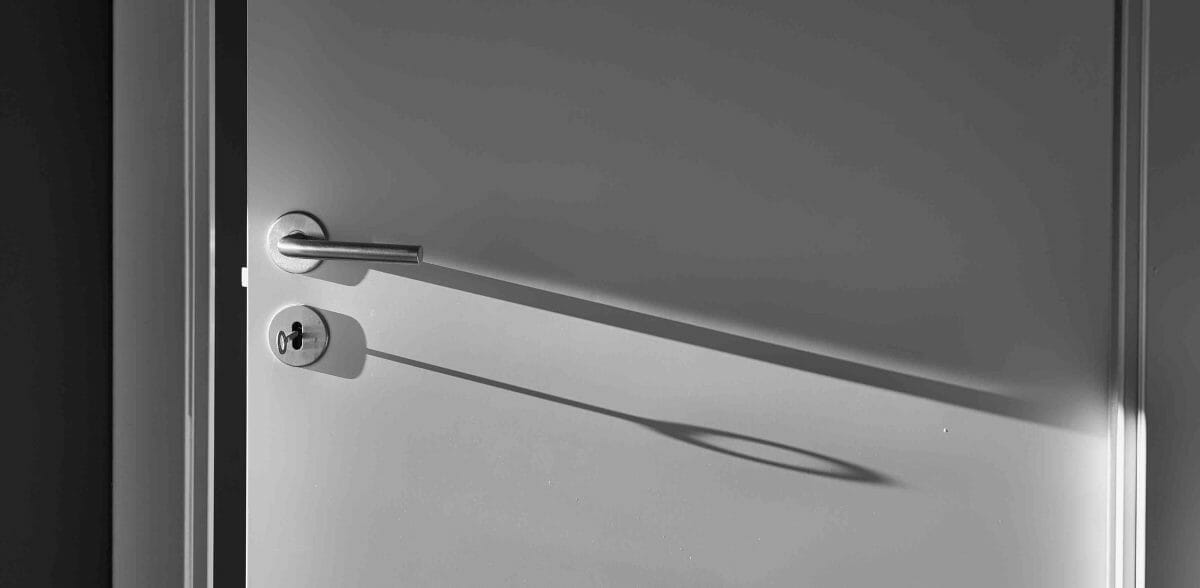
Curious minds always want to know the mechanisms that make equipment work. Beyond opening and closing your door, have you ever thought of how door locks work? It’s simple but complex. The latch stays partly in and out of the lock cylinder when the door is locked.
When you insert a key in the latch, it disengages and unlocks the door.
This article looks at locks, their parts, and how they work. Let’s dive right in!
A door lock has many parts. All come together to form the intricacies of the workings of a door lock. The door lock parts include the strike plate, keyway and rotor, cotter pin and spring, doorknob, cylinder, and bolt. When you insert the correct key, all these parts work together to lock or open the door.
Parts of a Door Lock
Before we look at how door locks work, let us first examine the different door lock parts. It becomes easier to understand the door locking mechanism when you know the features and functions.
Strike Plate

This is a metal plate on the door jamb. It is located directly opposite the lock. The strike plate is also the location where the latch sits when the door is open.
Keyway and Rotor
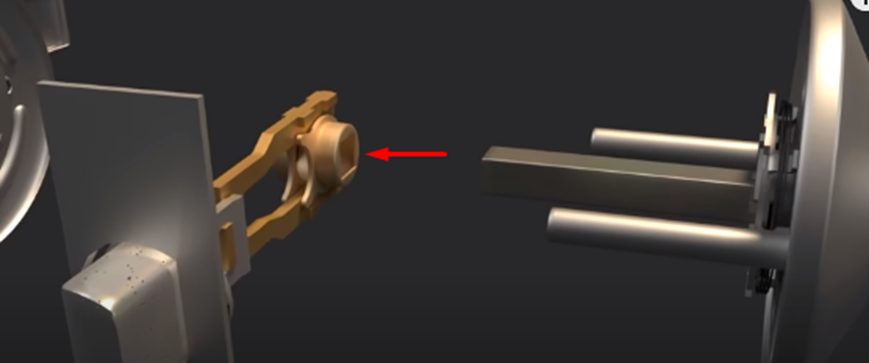
The keyway is a part of the lock. It is where you insert the key. The rotor, on the other hand, is the part that turns in the lock when you insert the correct key. It is found in the lock cylinder.
Cotter Pin and Spring
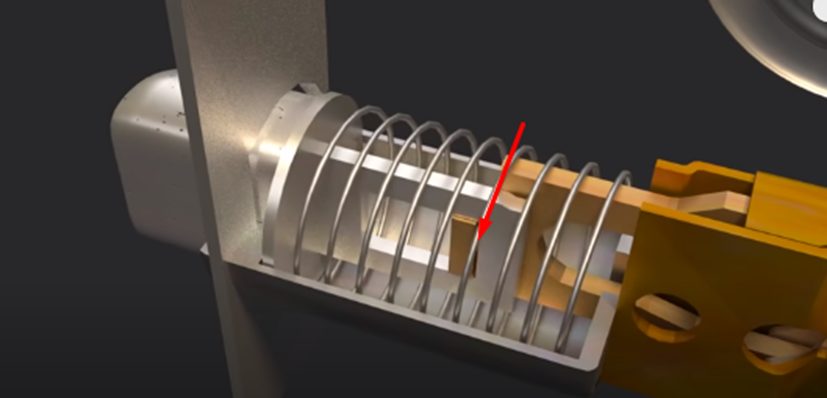
The cotter pin lines up with the grooves of the key when the spring is put under pressure. When you unlock the door, the cotter pin is responsible for turning the rotor. In contrast, the spring stops the rotor from turning except when the right key is used. (1)
Doorknob or Handle

The doorknob also called the handle, offers a grip when you want to open the door. A door has two doorknobs. The first is the outer knob, located on the outside of the door. The other is the interior knob, which is on the inside of the door. Doorknobs are mostly crafted with brass. (2)
Cylinder and Bolt
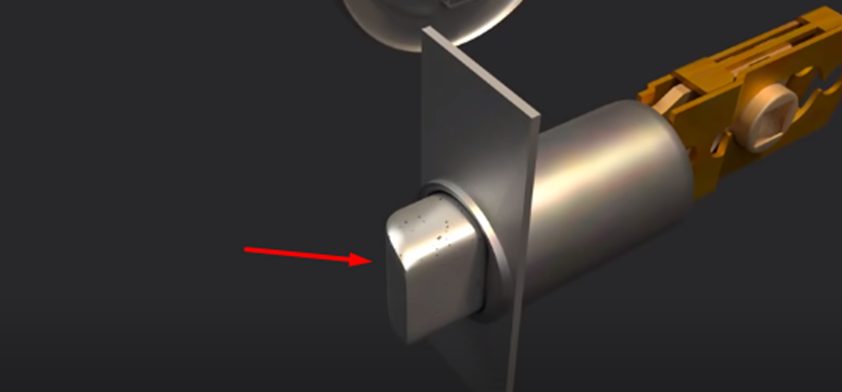
Also called the lock body, the cylinder comprises the locking mechanism of a door. It houses the spring-loaded pins that secure the lock. The spring-loaded pins make it impossible for the cylinder to turn without the correct key.
The bolt, on the other hand, stops the door from opening. It is also called the latch and it is pulled out right from the door jam when the knob is turned. If the door is locked, the latch will not disengage since you can’t turn the knob with the door locked.
How Door Locks Work
So, how does a door lock work? The mechanism is a bit complex. When a door lock is keyed into a locked position, the bolt is inside the strike plate and outside the lock cylinder. This makes it impossible for the door to open except if you insert the correct key. Different keys have different ridges’ patterns that fit into a particular lock.
When you lock the door, key locks function by turning the cylinder. The cylinder then discharges the spring after it’s turned to drive the bolt into a closed position. When the right key is inserted, it triggers the interior of the door lock mechanism and this unlocks the door.
The key aligns the pins when it is inserted in the keyway and this turns the cylinder to unlock the door. Inserting the wrong key will prevent the pins from aligning properly. Without proper alignment, there won’t be any gap between the lower and upper pins, and you won’t be able to turn the lock cylinder.
Wrapping Up
This article looks at the mechanism of how door locks work. It also looks at its parts and how each function complements the lock as a whole. Understanding the parts and mechanism of a door lock is the first step toward knowing how to fix a lock if it goes bad.
Take a look at some of our related articles below.
References
(1) under pressure – https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbescoachescouncil/
2017/07/28/18-ways-to-get-better-at-working-under-pressure/
(2) brass – https://www.britannica.com/technology/brass-alloy
Video Reference